veterinary dental x ray positioning pdf
Proper veterinary dental x-ray positioning is crucial for diagnostic accuracy‚ ensuring clear images of dental structures. It plays an essential role in modern veterinary practice‚ guiding effective treatment plans.
Key Concepts in Veterinary Dental Radiography
Key concepts in veterinary dental radiography include the bisecting angle technique‚ proper tube angulation‚ and sensor placement. The bisecting angle divides the angle between the teeth and film‚ ensuring accurate imaging. Tube angulation adjustments prevent foreshortening or elongation. Sensor placement must align with the dental structures‚ often parallel to the mandible or maxilla. Adhering to the ALARA principle minimizes radiation exposure. These principles ensure diagnostic-quality images‚ aiding in accurate diagnoses and effective treatment planning for veterinary dental patients.
The Importance of Proper X-Ray Positioning in Veterinary Dentistry
Proper x-ray positioning is essential for obtaining clear‚ diagnostic-quality images in veterinary dentistry. Accurate positioning ensures precise visualization of dental structures‚ enabling effective diagnosis of conditions like tooth fractures‚ abscesses‚ and bone loss. Misalignment can lead to distorted images‚ potentially causing misdiagnosis. Proper techniques also minimize radiation exposure to patients and personnel‚ aligning with the ALARA principle. Clear imaging enhances treatment planning‚ improves patient outcomes‚ and reduces the need for retakes‚ making it a cornerstone of modern veterinary dental care.
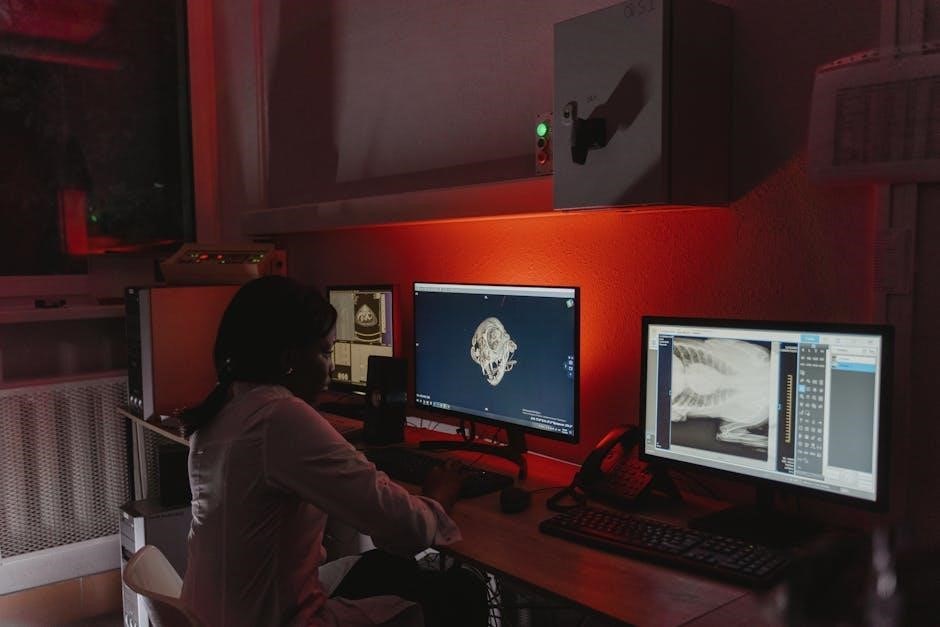

Equipment Setup for Veterinary Dental X-Ray
Dental x-ray units are wall-mounted‚ free-standing‚ or mobile‚ with handheld options available. They enable precise positioning of the x-ray beam and film for optimal imaging.
Components of a Dental X-Ray Unit
A dental x-ray unit consists of a control panel‚ x-ray tube‚ and positioning arm. The control panel regulates exposure settings‚ while the tube emits x-rays. Positioning arms allow precise angulation adjustments‚ ensuring accurate alignment with the patient. Accessories like sensors or film holders are essential for capturing images. These components work together to produce high-quality radiographs‚ aiding in accurate diagnoses of dental conditions in veterinary patients. Proper setup ensures minimal patient adjustment‚ optimizing efficiency and image clarity.
Positioning Tools and Accessories
Positioning tools include bite blocks‚ sensors‚ and film holders‚ which stabilize the patient and ensure accurate x-ray alignment. Sensors are placed lingually or palatally to image root apices‚ while bite blocks help maintain jaw alignment. Film packets contain filters and lead foil for radiation safety. Accessories like positioning guides and angulation markers aid in achieving the correct beam angle‚ ensuring optimal image quality. These tools are vital for minimizing retakes and maximizing diagnostic clarity in veterinary dental radiography.
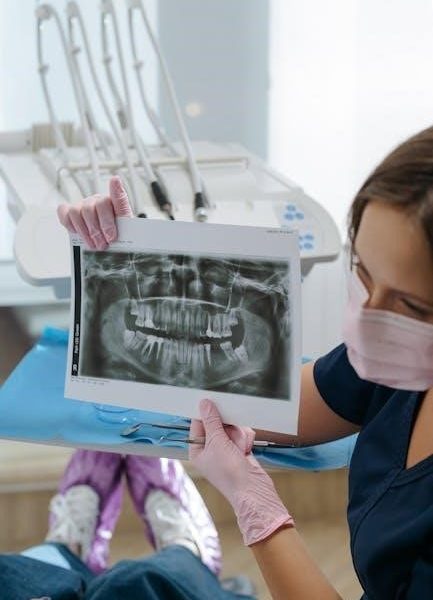
Patient Positioning Techniques
Proper patient positioning ensures accurate alignment of the x-ray beam with dental structures‚ minimizing distortion and enhancing diagnostic clarity in veterinary dental radiography.
General Principles of Patient Positioning
Proper patient positioning is critical for obtaining accurate radiographic images in veterinary dentistry. The fundamental principle involves aligning the x-ray beam perpendicular to the dental film or sensor‚ ensuring parallelism with the long axis of the tooth. This minimizes distortion and provides a true representation of dental structures. Positioning may require careful manipulation of the animal’s head and jaw to achieve optimal alignment. Additional considerations include sensor placement‚ beam angulation‚ and stabilization of the patient to avoid movement artifacts. These principles ensure clear‚ diagnostic-quality images for accurate assessments and effective treatment planning.
Specific Positioning for Canine and Feline Patients
Positioning techniques vary slightly between canine and feline patients due to anatomical differences. For canines‚ the sensor is often placed parallel to the mandible or maxilla‚ with the x-ray beam angled at 90 degrees to the bisecting angle. Feline patients require more precise adjustments due to their smaller size‚ often involving a slightly caudal beam angulation to capture the entire dental structure. Proper alignment ensures clear visualization of root apices and surrounding bone‚ essential for diagnosing conditions like periodontal disease or dental fractures. These species-specific approaches enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
Advanced Positioning Strategies for Challenging Patients
Challenging patients‚ such as uncooperative animals or those with unusual anatomy‚ require tailored positioning strategies. Techniques include adjusting tube angulation to accommodate irregular jaw alignment and using sedation for immobilization. Customized approaches ensure accurate imaging‚ minimizing retakes. Advanced methods focus on optimizing beam alignment and sensor placement to capture clear images of complex dental structures‚ even in difficult cases.
Image Acquisition and Angulation
Accurate image acquisition relies on proper angulation‚ ensuring clear visualization of dental structures. Techniques like the bisecting angle method guide optimal positioning for precise diagnostic imaging in veterinary dentistry.
Bisecting Angle Technique in Dental Radiography
The bisecting angle technique is a fundamental method in dental radiography‚ ensuring accurate imaging by dividing the angle between the teeth and the film. This technique involves directing the X-ray beam at a 90-degree angle to the bisecting line‚ which equally splits the angle formed by the dental structures and the imaging sensor. Proper alignment minimizes distortion‚ providing clear visualization of tooth roots and surrounding bone. This method is essential for diagnostic accuracy‚ reducing positioning errors and enhancing the quality of radiographic images in veterinary dentistry.
Adjusting Tube Angulation for Optimal Imaging
Accurate tube angulation is critical for obtaining high-quality radiographic images in veterinary dentistry. Incorrect angulation can lead to foreshortening or elongation of structures‚ distorting the image. By adjusting the tube head angle‚ practitioners can align the X-ray beam perpendicular to the bisecting angle‚ ensuring proper representation of dental anatomy. This technique minimizes distortion and enhances diagnostic clarity. Proper angulation also adheres to the ALARA principle‚ optimizing radiation safety while maintaining image quality for accurate patient assessment and treatment planning.
Common Errors and Corrections in X-Ray Positioning
Common errors include improper tube angulation‚ misalignment‚ and incorrect sensor placement‚ leading to distorted images. Adjusting the angle and ensuring proper alignment corrects these issues effectively.
Identifying and Correcting Positioning Errors
- Positioning errors commonly arise from improper tube angulation‚ misalignment‚ or incorrect sensor placement‚ leading to distorted images.
- Foreshortening or elongation can be corrected by adjusting the tube angle and ensuring proper alignment with the bisecting angle technique.
- Improper sensor placement‚ such as being too deep or misaligned‚ can cause inadequate visualization of root apices.
- Lateral adjustments to the tube head can help elongate root structures for clearer imaging.
- Proper alignment of the collimator with the bisecting angle ensures parallelism to the dental arch‚ minimizing errors.
- Regular practice and adherence to positioning guides help refine techniques and reduce common mistakes.
Understanding Foreshortening and Elongation in Images
Foreshortening and elongation are common imaging artifacts in dental radiography‚ affecting the accuracy of diagnoses. Foreshortening occurs when the X-ray beam is angled too steeply‚ making roots appear shorter than they are. Conversely‚ elongation happens with a shallow beam angle‚ causing roots to seem longer. Both issues stem from improper tube angulation relative to the dental arch. Correcting these requires adjusting the tube head position to align with the bisecting angle technique‚ ensuring accurate representation of dental structures for reliable diagnostic outcomes.
Radiation Safety and Protection
Radiation safety is paramount in veterinary dental radiography. Adhering to the ALARA principle minimizes exposure. Protective measures include shielding and maintaining a 6-foot distance from the X-ray source during image acquisition.
ALARA Principle in Veterinary Dental Radiography
The ALARA principle (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) is central to radiation safety‚ emphasizing minimal exposure while obtaining diagnostic-quality images. It involves using the lowest necessary radiation dose‚ ensuring safety for both patients and personnel. Techniques include precise beam collimation‚ digital sensors‚ and shielding. Personnel should maintain a distance of at least 6 feet from the X-ray source during imaging. Regular training and proper equipment maintenance further support ALARA compliance‚ reducing risks while maintaining image quality for accurate diagnoses.
Protective Measures for Personnel and Patients
Protective measures in veterinary dental radiography are essential to minimize radiation exposure. Personnel should wear lead aprons‚ thyroid collars‚ and gloves‚ while maintaining a distance of at least 6 feet from the X-ray source. Patients are protected by using digital sensors‚ which reduce radiation doses‚ and collimating the X-ray beam to the smallest necessary size. Regular training and equipment checks ensure safety protocols are followed‚ safeguarding both staff and animals while maintaining image quality for accurate diagnoses.
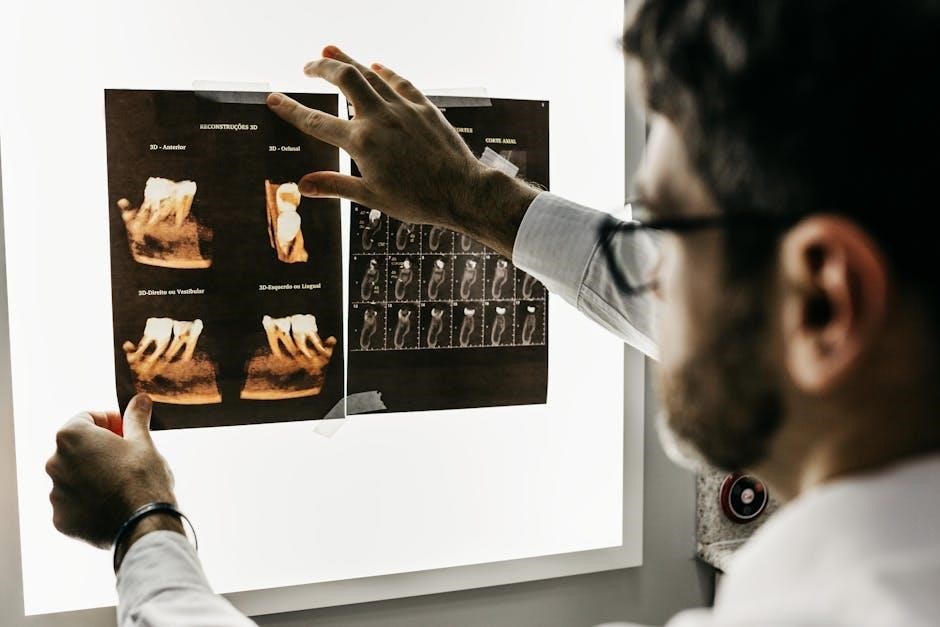
Case Studies and Practical Examples
Case studies demonstrate proper veterinary dental X-ray positioning techniques‚ showcasing real-world applications. Practical examples highlight diagnostic accuracy in identifying dental conditions‚ ensuring effective treatment plans for pets.
Real-World Applications of Proper X-Ray Positioning
Proper X-ray positioning is vital in diagnosing dental conditions like caries‚ fractures‚ and periodontal disease. Accurate imaging helps identify root elongation or foreshortening‚ guiding precise treatment plans. Techniques like the bisecting angle ensure clear visualization of tooth roots and surrounding structures‚ aiding in surgical decisions. Correct positioning also minimizes retakes‚ reducing radiation exposure and improving patient safety. Real-world examples include imaging canine mandibles and feline maxillas‚ where precise alignment ensures diagnostic accuracy‚ enabling effective treatment outcomes for pets.
Common Dental Conditions Diagnosed via X-Ray
Dental X-rays are essential for diagnosing conditions like tooth fractures‚ periodontal disease‚ and root elongation. They reveal caries‚ resorption‚ and bone loss‚ aiding in precise treatment planning. Proper positioning ensures clear visualization of structures‚ helping identify issues early. X-rays are particularly useful in detecting asymptomatic pathologies‚ such as hidden fractures or abscesses‚ which are critical for improving patient outcomes in veterinary care.
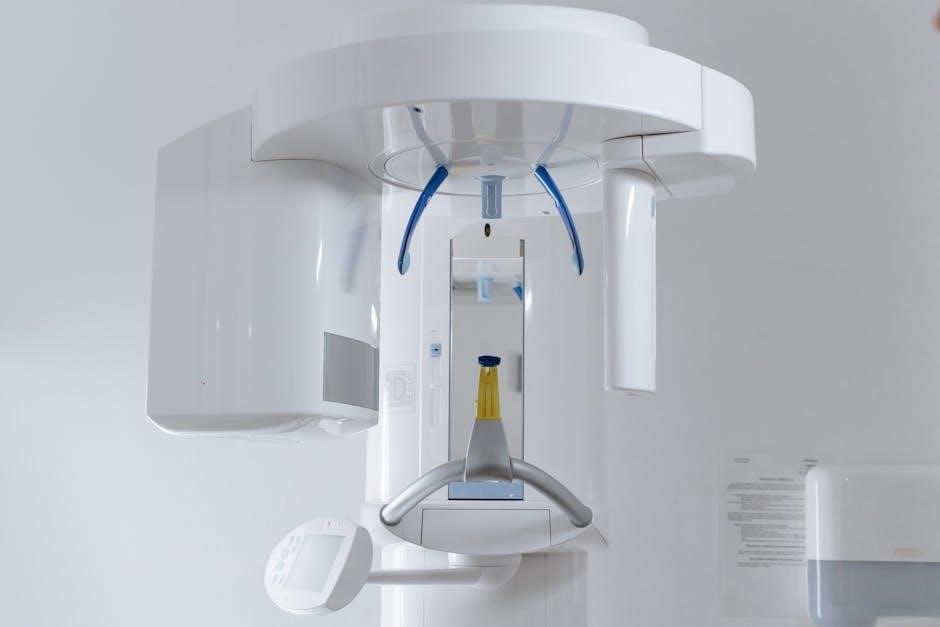
Future Trends in Veterinary Dental Imaging
Advancements in digital radiography and cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) are revolutionizing veterinary dental imaging‚ offering higher resolution and 3D capabilities. These technologies enhance diagnostic accuracy and improve treatment planning‚ enabling better visualization of complex dental structures. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in image analysis is also emerging‚ aiding in faster and more precise diagnostics. These innovations are expected to significantly advance the field‚ providing veterinarians with cutting-edge tools for improved patient care.
Advancements in Digital Radiography
Digital radiography has significantly advanced veterinary dental imaging‚ offering higher-resolution images with reduced radiation exposure. Modern systems feature faster processing times and integrated software for enhanced image clarity‚ aiding in early detection of conditions like tooth resorption or fractures. These technologies improve diagnostic accuracy‚ support the ALARA principle for safer practices‚ and facilitate more efficient treatment planning‚ making them indispensable in contemporary veterinary care.
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) in Veterinary Dentistry
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) revolutionizes veterinary dentistry by providing 3D imaging of dental structures‚ offering unparalleled detail compared to traditional 2D radiographs. CBCT is particularly useful for evaluating complex dental anomalies‚ fractures‚ and sinus involvement; Its ability to reconstruct images in multiple planes aids in precise diagnostic and treatment planning. Despite its advantages‚ CBCT is typically reserved for challenging cases where standard radiography is insufficient‚ ensuring optimal use of advanced imaging technology in veterinary care.
Mastery of veterinary dental x-ray positioning enhances diagnostic accuracy. Utilize detailed guides and resources for continuous learning and refinement of imaging techniques in veterinary dentistry.
Proper veterinary dental x-ray positioning ensures accurate diagnostics. Use the bisecting angle technique‚ position sensors parallel to dental structures‚ and adjust beam angles for clear images. Always follow ALARA principles for radiation safety. Regularly review guides and manuals for updates and best practices. Continuous learning enhances skill and improves patient care outcomes in veterinary dentistry. Utilize available resources like the FREE guide to perfect veterinary dental x-ray positioning for detailed instructions and clear diagrams to refine techniques.
Recommended Resources for Further Learning
Enhance your skills with the FREE Guide to Perfect Veterinary Dental X-Ray Positioning‚ offering clear diagrams and instructions. Explore resources like the Air Techniques Veterinary Dental X-Ray System Manual for detailed protocols. The Beyond the Crown Veterinary Education platform provides comprehensive tutorials. Additionally‚ the EzRay Air VET System Guide and Easy Guide to Dental X-Ray Positioning by Mary L. Berg‚ RVT‚ are invaluable. These resources ensure you stay updated and proficient in veterinary dental radiography techniques.
Related posts:
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.